Windows 7 has the best built-in backup options of any Windows version yet.
This post will show you those options and provide my recommendation for a better alternative.
(*File descriptions were taken from the Windows 7 help files)
File backup
Windows Backup allows you to make copies of data files for all people that use the computer. You can let Windows choose what to back up or you can select the individual folders, libraries, and drives that you want to back up. By default, your backups are created on a regular schedule. You can change the schedule and you can manually create a backup at any time. Once you set up Windows Backup, Windows keeps track of the files and folders that are new or modified and adds them to your backup.
See my guide: Backup Using Windows 7 Backup And Restore
Better Alternative To File backup: Cobian Backup and SyncToy
System image backup
Windows Backup provides you with the ability to create a system image, which is an exact image of a drive. A system image includes Windows and your system settings, programs, and files. You can use a system image to restore the contents of your computer if your hard drive or computer ever stops working. When you restore your computer from a system image, it is a complete restoration; you can’t choose individual items to restore, and all of your current programs, system settings, and files are replaced. Although this type of backup includes your personal files, we recommend that you back up your files regularly using Windows Backup so that you can restore individual files and folders as needed. When you set up scheduled file backup, you can choose whether you want to include a system image. This system image only includes the drives required for Windows to run. You can manually create a system image if you want to include additional data drives.*
See my guide: Using Windows 7 System Image
Better Alternative to System Image backup: Acronis True Image Home
Previous versions
Previous versions are copies of files and folders that Windows automatically saves as part of system protection. You can use previous versions to restore files or folders that you accidentally modified or deleted, or that were damaged. Depending on the type of file or folder, you can open, save to a different location, or restore a previous version. Previous versions can be helpful, but should not be considered a backup because the files get replaced by new versions and will not be available if the drive were to fail.*
To be clear: You must have System Protection enabled to use Previous Versions.
What are previous versions?
Previous versions are either copies of files and folders created by Windows Backup or copies of files and folders that Windows automatically saves as part of a restore point. You can use previous versions to restore files and folders that you accidentally modified or deleted, or that were damaged. Depending on the type of file or folder, you can open, save to a different location, or restore a previous version.*
How are previous versions created?
Previous versions are automatically saved as part of a restore point. If system protection is turned on, Windows automatically creates previous versions of files and folders that have been modified since the last restore point was made. Typically, restore points are made once a day. If your disk is partitioned or if you have more than one hard disk on your computer, you need to turn on system protection for the other partitions or disks. Previous versions are also created by Windows Backup when you back up your files.*
Right-click on a file and choose Properties then the Previous Versions tab.
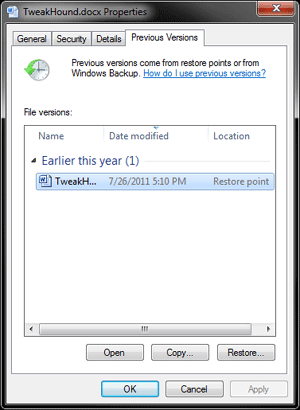
See the next section (System Restore) to see how to configure Previous Versions.
Better Alternative to Previous Versions – None
System Restore
System Restore helps you restore your computer’s system files to an earlier point in time. It’s a way to undo system changes to your computer without affecting your personal files, such as e‑mail, documents, or photos. System Restore uses a feature called system protection to regularly create and save restore points on your computer. These restore points contain information about registry settings and other system information that Windows uses. You can also create restore points manually.*
Better Alternative to System Restore: For the OS itself a system image is a far better alternative. However the Previous Versions feature requires this.
I recommend the average user use both System Restore and a system image.
To configure System Restore:
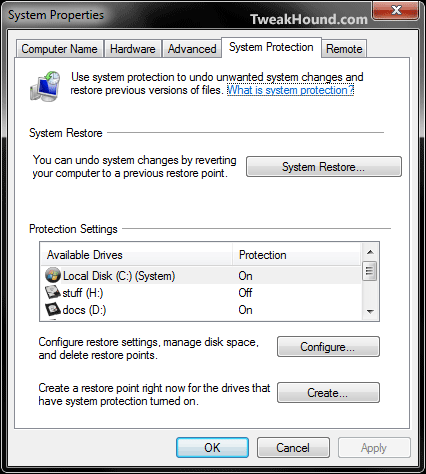
Go to: Start button > Control Panel > System and Maintenance > System > System Protection
Get there quick: Press the Windows + R keys and type (or copy/paste) SystemPropertiesProtection.exe
Highlight the drives you wish to enable System Restore on and click Configure.
Turn off System Protection on any drives you don’t want protected the same way.
If you have moved your Libraries to another drive and want to use the Previous Versions feature on those files be sure to enable System Protection on those drives.
Further information – Make use of the Help files. A wealth of information is there!
-END-